Hammer Toe Treatment Without Surgery
 Overview
Overview
A Hammer toe is commonly mistaken as any type of toe deformity. The terms claw toe, or mallet toe, although technically different than a hammer toe, are commonly referred as such. The toe may be flexible with movement at the joints, or it may be rigid, especially if it has been present for a long time. With a true hammertoe the deformity exists at the proximal interphalangeal joint only.
Causes
Hammertoes are usually structural in nature. Many times this is the foot structure you were born with and other factors have now made it so that symptoms appear. The muscles in your foot may become unbalanced over time, allowing for a deformity of the small bones in each toe. With longstanding deformity the toe may become rigid. Sometimes one toe is longer than another and this causes a buckling of the digit. A hammertoe may also be caused by other foot deformities such as a bunion. Trauma or other surgery of your foot may predispose you to having the condition if your foot structure is altered.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Hammer toes can cause problems with walking and lead to other foot problems, such as blisters, calluses, and sores. Pain is caused by constant friction over the top of the toe?s main joint. It may be difficult to fit into some shoe gear due to the extra space required for the deformed toe. In many cases there will be pain on the ball of the foot over the metatarsals along with callus formation. This is due to the toes not functioning properly, failing to properly touch the ground during the gait cycle. The ball of the foot then takes the brunt of the ground forces, which causes chronic pain.
Diagnosis
Hammertoes are progressive, they don?t go away by themselves and usually they will get worse over time. However, not all cases are alike, some hammertoes progress more rapidly than others. Once your foot and ankle surgeon has evaluated your hammertoes, a treatment plan can be developed that is suited to your needs.
Non Surgical Treatment
Early on, when a hammertoe first starts and is still flexible, here are some ways it might be treated. Your healthcare provider may splint or tape the toe into the correct, normal position. You can use your fingers to stretch your toes and toe joints toward a more normal position. Exercise your toes by trying to pick up marbles with them or by wadding up a towel on the floor with your toes. Padding may be used to change where your weight falls when you walk on the foot.
Surgical Treatment
If these non-invasive treatments don?t work, or if the joint is rigid, a doctor?s only recourse may be to perform surgery. During the surgery, the doctor makes an incision and cuts the tendon to release it or moves the tendon away from or around the joint. Sometimes part of the joint needs to be removed or the joint needs to be fused. Each surgery is different in terms of what is needed to treat the hammertoe. Normally after any foot surgery, patients use a surgical shoe for four to six weeks, but often the recovery from hammertoe surgery is more rapid than that. An unfortunate reality is that hammertoe can actually return even after surgery if a patient continues to make choices that will aggravate the situation. Though doctors usually explain pretty clearly what needs to be done to avoid this.
 Prevention
Prevention
There are several things you can do to help prevent hammer toes from forming or progressing. Wear supportive shoes to help prevent deformities. Hammer toes are often related to faulty foot mechanics, especially foot flattening. Wear custom orthotics prescribed by your podiatrist. Orthotics may slow the progression or prevent the development of hammer toes. Avoid shoes with narrow or pointed toe boxes that can compress the toes.
Find Out About Overpronation
As with the "normal pronation" sequence, the outside of the heel makes the initial ground contact. However, the foot rolls inward more than the ideal fifteen percent, which is called "overpronation." This means the foot and ankle have problems stabilizing the body, and shock isn't absorbed as efficiently. At the end of the gait cycle, the front of the foot pushes off the ground using mainly the big toe and second toe, which then must do all the work.
Causes
Unless there is a severe, acute injury, overpronation develops as a gradual biomechanical distortion. Several factors contribute to developing overpronation, including tibialis posterior weakness, ligament weakness, excess weight, pes planus (flat foot), genu valgum (knock knees), subtalar eversion, or other biomechanical distortions in the foot or ankle. Tibialis posterior weakness is one of the primary factors leading to overpronation. Pronation primarily is controlled by the architecture of the foot and eccentric activation of the tibialis posterior. If the tibialis posterior is weak, the muscle cannot adequately slow the natural pronation cycle.
Symptoms
In addition to problems overpronation causes in the feet, it can also create issues in the calf muscles and lower legs. The calf muscles, which attach to the heel via the Achilles tendon, can become twisted and irritated as a result of the heel rolling excessively toward the midline of the body. Over time this can lead to inflexibility of the calf muscles and the Achilles tendon, which will likely lead to another common problem in the foot and ankle complex, the inability to dorsiflex. As such, overpronation is intrinsically linked to the inability to dorsiflex.
Diagnosis
Look at your soles of your footwear: Your sneaker/shoes will display heavy wear marks on the outside portion of the heel and the inside portion above the arch up to the top of the big toe on the sole. The "wet-foot" test is another assessment. Dip the bottom of your foot in water and step on to a piece of paper (brown paper bag works well). Look at the shape of your foot. If you have a lot of trouble creating an arch, you likely overpronate. An evaluation from a professional could verify your foot type.

Non Surgical Treatment
When you see the doctor, he or she will likely perform a complete examination of your feet and watch you walk. The doctor will need to take x-rays to determine the cause of your flat feet. In some cases, further imaging may be needed, especially if your symptoms are severe and sudden in nature. Once you are properly diagnosed, your doctor will create an appropriate treatment plan. There are several options to correct overpronation, such as orthotics. In many cases, overpronation can be treated with non-surgical methods and over-the-counter orthotics. In severe cases, however, custom-made orthotics may work better. Orthotics provide arch support and therefore prevent collapse of the arch with weight bearing. They are made of materials such as spongy rubber or hard plastic. Your doctor will also want to examine your footwear to ensure they fit properly and offer enough medial support. Extra support and stability can be achieved with footwear that has a firm heel counter. If you are experiencing pain, you should be able to use over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen to relieve symptoms.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. Primary benefit is that yje surgery is minimally invasive and fully reversible. the primary risk is a high chance of device displacement, generally not tolerated in adults.
An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer.
Will Severs Disease Need To Have Surgical Treatments?
Sever's disease (calcaneal apophysitis) is an inflammatory condition that affects the heel bone (calcaneus). It happens frequently in young athletes between the ages of 10 and 13, causing pain in one or both heels when walking. Tenderness and swelling may also be present. Similar to another overuse condition, Osgood-Schlatter disease, Sever's disease has occasionally been termed Osgood-Schlatter of the heel. In young people, the heel bones are still divided by a layer of cartilage. During the growth years, the bone is growing faster than tendons. This makes it likely that the heel cord will be applying great tension where it inserts into the heel bone. In addition, the heel cord is attached to an immature portion of the heel bone, the calcaneal apophysis. In young athletes, the repetitive stress of running and jumping while playing soccer and basketball may cause an inflammation of the growth center of the heel.
Causes
Sever?s disease is common, and typically occurs during a child?s growth spurt, which can occur between the ages of 10 and 15 in boys and between the ages of 8 and 13 in girls. Feet tend to grow more quickly than other parts of the body, and in most kids the heel has finished growing by the age of 15. Being active in sports or participating in an activity that requires standing for long periods can increase the risk of developing Sever?s disease. In some cases, Sever?s disease first becomes apparent after a child begins a new sport, or when a new sports season starts. Sports that are commonly associated with Sever?s disease include track, basketball, soccer, and gymnastics. Children who are overweight or obese are also at a greater risk of developing this condition. Certain foot problems can also increase the risk, including. Over pronating. Kids who over pronate (roll the foot inward) when walking may develop Sever?s disease. Flat foot or high arch. An arch that is too high or too low can put more stress on the foot and the heel, and increase the risk of Sever?s disease. Short leg. Children who have one leg that is shorter than the other may experience Sever?s disease in the foot of the shorter leg because that foot is under more stress when walking.
Symptoms
Typically, the sports injury occurs where the achilles tendon attaches to the bone. The epiphyseal growth plate is located at the end of a developing bone where cartilage turns into bone cells. As the growth center expands and unites, this area may become inflamed, causing severe pain when both sides of the heel are compressed. There is typically no swelling and no warmth, so it?s not always an easy condition to spot. The child usually has trouble walking, stiffness upon waking, and pain with activity that subsides during periods of rest.
Diagnosis
It is not difficult for a doctor to diagnose Sever's disease in a youngster or teenager. A personal history and a physical examination are usually all it takes to determine the cause of heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
The immediate goal of treatment is pain relief. Because symptoms generally worsen with activity, the main treatment for Sever's disease is rest, which helps to relieve pressure on the heel bone, decreasing swelling and reducing pain. As directed by the doctor, a child should cut down on or avoid all activities that cause pain until all symptoms are gone, especially running barefoot or on hard surfaces because hard impact on the feet can worsen pain and inflammation. The child might be able to do things that do not put pressure on the heel, such as swimming and biking, but check with a doctor first. The doctor might also recommend that a child with Sever's disease perform foot and leg exercises to stretch and strengthen the leg muscles and tendons, elevate and apply ice (wrapped in a towel, not applied directly to the skin) to the injured heel for 20 minutes two or three times per day, even on days when the pain is not that bad, to help reduce swelling, use an elastic wrap or compression stocking that is designed to help decrease pain and swelling, take an over-the-counter medicine to reduce pain and swelling, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin). Children should not be given aspirin for pain due to the risk of a very serious illness called Reye syndrome. In very severe cases, the doctor might recommend that the child wear a cast for anywhere from 2 to 12 weeks to immobilize the foot so that it can heal.
Exercise
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with Severs disease. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 1 - 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms. Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate, advanced and other exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this stretch in long sitting with your leg to be stretched in front of you. Your knee and back should be straight and a towel or rigid band placed around your foot as demonstrated. Using your foot, ankle and the towel, bring your toes towards your head as far as you can go without pain and provided you feel no more than a mild to moderate stretch in the back of your calf, Achilles tendon or leg. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times at a mild to moderate stretch provided the exercise is pain free. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this exercise with a resistance band around your foot and your foot and ankle held up towards your head. Slowly move your foot and ankle down against the resistance band as far as possible and comfortable without pain, tightening your calf muscle. Very slowly return back to the starting position. Repeat 10 - 20 times provided the exercise is pain free. Once you can perform 20 repetitions consistently without pain, the exercise can be progressed by gradually increasing the resistance of the band provided there is no increase in symptoms. Bridging. Begin this exercise lying on your back in the position demonstrated. Slowly lift your bottom pushing through your feet, until your knees, hips and shoulders are in a straight line. Tighten your bottom muscles (gluteals) as you do this. Hold for 2 seconds then slowly lower your bottom back down. Repeat 10 times provided the exercise is pain free.
What Are The Causes And Signals Of A Ruptured Achilles Tendon?
Overview
 Complete Achilles tendon ruptures occur most commonly at the mid-substance, but also distally at the insertion site or proximally at the myotendinous junction. These can be traumatic and devastating injuries, resulting in significant pain, disability, and healthcare cost. As many as 2.5 million individuals sustain Achilles tendon ruptures each year and the incidence is rising. This trend is due, in part, to an increase in athletic participation across individuals of all ages.
Complete Achilles tendon ruptures occur most commonly at the mid-substance, but also distally at the insertion site or proximally at the myotendinous junction. These can be traumatic and devastating injuries, resulting in significant pain, disability, and healthcare cost. As many as 2.5 million individuals sustain Achilles tendon ruptures each year and the incidence is rising. This trend is due, in part, to an increase in athletic participation across individuals of all ages.
Causes
As with any muscle or tendon in the body, the Achilles tendon can be torn if there is a high force or stress on it. This can happen with activities which involve a forceful push off with the foot, for example, in football, running, basketball, diving, and tennis. The push off movement uses a strong contraction of the calf muscles which can stress the Achilles tendon too much. The Achilles tendon can also be damaged by injuries such as falls, if the foot is suddenly forced into an upward-pointing position, this movement stretches the tendon. Another possible injury is a deep cut at the back of the ankle, which might go into the tendon. Sometimes the Achilles tendon is weak, making it more prone to rupture. Factors that weaken the Achilles tendon are corticosteroid medication (such as prednisolone), mainly if it is used as long-term treatment rather than a short course. Corticosteroid injection near the Achilles tendon. Certain rare medical conditions, such as Cushing?s syndrome, where the body makes too much of its own corticosteroid hormones. Increasing age. Tendonitis (inflammation) of the Achilles tendon. Other medical conditions which can make the tendon more prone to rupture, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, gout and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) - lupus. Certain antibiotic medicines may slightly increase the risk of having an Achilles tendon rupture. These are the quinolone antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin. The risk of having an Achilles tendon rupture with these antibiotics is actually very low, and mainly applies if you are also taking corticosteroid medication or are over the age of about 60.
Symptoms
A person with a ruptured Achilles tendon may experience one or more of the following. Sudden pain (which feels like a kick or a stab) in the back of the ankle or calf, often subsiding into a dull ache. A popping or snapping sensation. Swelling on the back of the leg between the heel and the calf. Difficulty walking (especially upstairs or uphill) and difficulty rising up on the toes. These symptoms require prompt medical attention to prevent further damage. Until the patient is able to see a doctor, the "R.I.C.E." method should be used. This involves, rest. Stay off the injured foot and ankle, since walking can cause pain or further damage. Ice. Apply a bag of ice covered with a thin towel to reduce swelling and pain. Do not put ice directly against the skin. Compression. Wrap the foot and ankle in an elastic bandage to prevent further swelling. Elevation. Keep the leg elevated to reduce the swelling. It should be even with or slightly above heart level.
Diagnosis
If an Achilles tendon rupture is suspected, it is important to consult a doctor straight away so that an accurate diagnosis can be made and appropriate treatment recommended. Until a doctor can be consulted it is important to let the foot hang down with the toes pointed to the ground. This prevents the ends of the ruptured tendon pulling any farther apart. The doctor will take a full medical history, including any previous Achilles tendon injuries and what activity was being undertaken at the time the present injury occurred. The doctor will also conduct a physical examination and will check for swelling, tenderness and range of movement in the lower leg and foot. A noticeable gap may be able to be felt in the tendon at the site of the rupture. This is most obvious just after the rupture has occurred and swelling will eventually make this gap difficult to feel. One test commonly used to confirm an Achilles tendon rupture is the Thomson test. For this test the patient lies face down on an examination table. The doctor then squeezes the calf muscles; an action that would normally cause the foot to point like a ballerina (plantar flexion). When a partial rupture has occurred the foot's ability to point may be decreased. When a complete rupture has occurred, the foot may not point at all. Ultrasound scanning of the Achilles tendon may also be recommended in order to assist with the diagnosis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Non-surgical management traditionally was selected for minor ruptures, less active patients, and those with medical conditions that prevent them from undergoing surgery. It traditionally consisted of restriction in a plaster cast for six to eight weeks with the foot pointed downwards (to oppose the ends of the ruptured tendon). But recent studies have produced superior results with much more rapid rehabilitation in fixed or hinged boots. 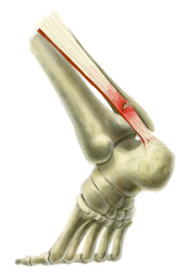
Surgical Treatment
Operative treatment of Achilles tendon ruptures involves opening the skin and identifying the torn tendon. This is then sutured together to create a stable construct. This can be performed through a standard Achilles tendon repair technique or through a mini-incision technique (to read about the different types of techniques, look under ?Procedure? in Achilles Tendon Repair). By suturing the torn tendon ends together, they maintain continuity and can be mobilized more quickly. However, it is critical to understand that the return to normal activities must wait until adequate healing of the tendon has occurred. The potential advantages of an open repair of the Achilles tendon include, faster recovery, this means that patients will lose less strength. Early Range of Motion. They are able to move the ankle earlier so it is easier to regain motion. Lower Re-rupture Rate. The re-rupture rate may be significantly lower in operatively treated patients (2-5%) compared to patients treated non-operatively (8-15%). The main disadvantage of an open repair of the Achilles tendon rupture is the potential for a wound-healing problem which could lead to a deep infection that is difficult to eradicate, or a painful scar.
Prevention
Here are some suggestions to help to prevent this injury. Corticosteroid medication such as prednisolone, should be used carefully and the dose should be reduced if possible. But note that there are many conditions where corticosteroid medication is important or lifesaving. Quinolone antibiotics should be used carefully in people aged over 60 or who are taking steroids.